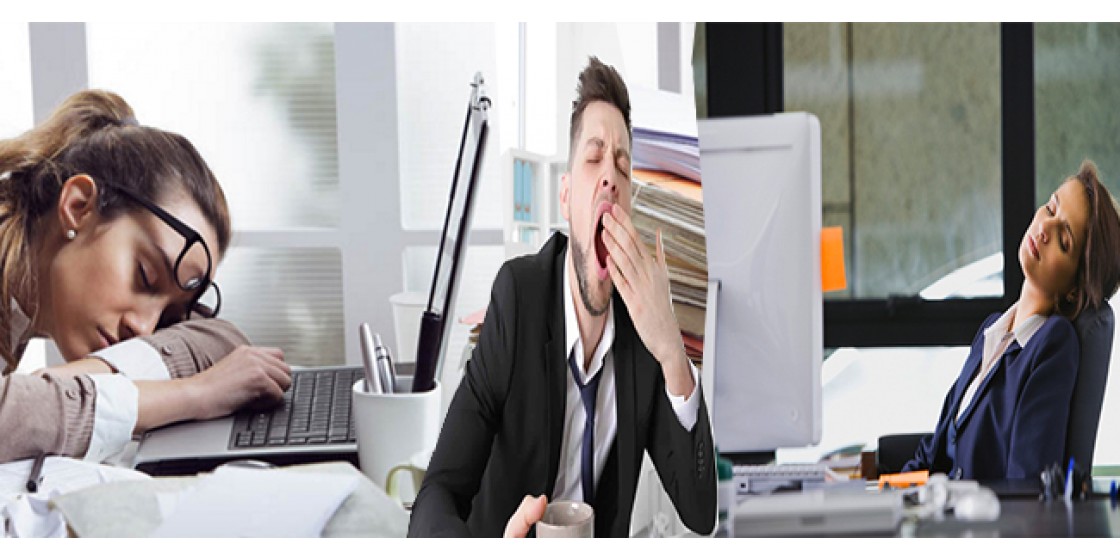
What is Sleep Deprivation?
- Sleep deprivation happens when you don’t get enough sleep for your body to function properly.
- Unfortunately, facts on the prevalence of sleep deprivation show that many of us are at risk from not getting enough sleep. Doctors from the NHS say that about 1 in 3 adults suffer from the consequences of sleep deprivation.
- The journal PLoS One says that you need between 7 and 8 hours of good quality sleep every night. Regularly sleeping less than 6 hours a night can put you at risk from the dangers of sleep deprivation such as diabetes, heart disease or stroke.
- According to the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, getting enough sleep is essential for good health. Sleep is a basic need of the body, and the effects of sleep deprivation can be as serious as not eating or breathing. Not sleeping enough affects your physical and mental health and can lead to loss of productivity and serious injury.
- The effects of poor sleep can also build up over time. Although napping can help to reduce some of the effects of little sleep, it is not a substitute for getting a good night’s sleep regularly.
- There are also different stages to your sleep – rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and non-rapid eye movement sleep. REM sleep is generally the time when your brain is active during sleep and you dream. Non-REM sleep is a deeper sleep when your body and mind repair themselves.
- One study found that sleep deprivation during different sleep stages affects your mind in different ways. For example, loss of sleep in the REM stage can affect learning ability.
Causes of Sleep Deprivation
- There can be many reasons why you are not getting your required 7 or 8 hours of sleep every night.
- Doctors from the Victoria State Government say that lifestyle choices often result in not getting enough sleep. Staying up late to socialize, watch TV, or work can start to impact negatively on your health.
- The physical symptoms of sleep deprivation could be felt if you have an underlying illness or take medication that causes insomnia. Also, taking stimulants such as alcohol, caffeinated drinks, or smoking before bedtime can result in poor sleep quality.
- Other reasons for being deprived of sleep include having young children, anxiety, or suffering from a sleep disorder.
Symptoms and Signs of Sleep Deprivation
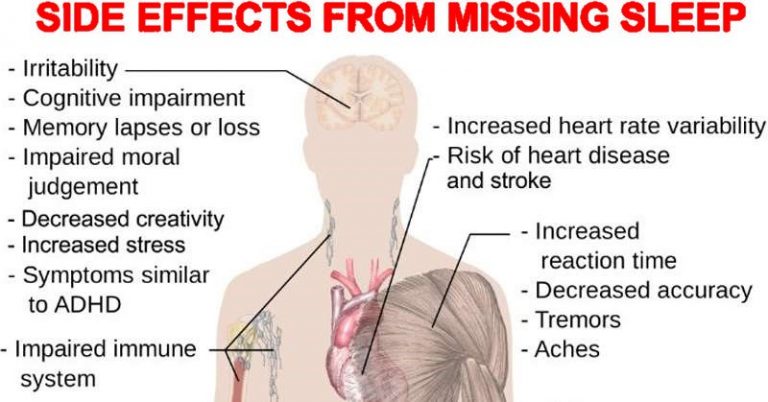
- The immediate symptoms of not sleeping enough can be tiredness, irritability, poor concentration, and napping during the day.
- If you go a few days of not getting enough sleep or you have erratic sleep patterns, the signs of sleep deprivation can be more serious. Doctors say that over time, sleep deprivation can cause a lack of alertness, poor memory, increased anxiety, and poor coordination.
The Effects of Sleep Deprivation
- Let’s look in more detail at the effects of sleep deprivation and what you can do to combat them.
Lack of Sleep Can Cause Weight Gain
- Putting on extra weight is one of the physical effects of sleep deprivation.
- One of the reasons why chronic sleep deficiency causes you to be overweight is that it affects your hormones. Studies report that the hunger hormone ghrelin increases when you are deprived of sleep. At the same time, lack of sleep inhibits leptin – the hormone that makes you feel full. This hormonal imbalance can lead to overeating and obesity.
- One cohort study involving over 1,000 adults found that short sleep is associated with an increased risk of weight gain. Sleeping 5 hours or less increased ghrelin and decreased leptin hormones which are linked to increased incidences of obesity.
- Sleep deprivation can affect your weight because it also affects glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity. This lack of sleep can cause fat accumulation and increase your risk of obesity complications.
- Studies about the negative effects of sleep loss say that, although sleep is a sedentary activity, enjoying plenty of sleep can protect you from being overweight.
- Getting adequate sleep every night is a simple lifestyle choice that promotes weight loss. Also learn how to boost your weight-loss efforts by increasing the amount you walk daily.
Long Term Sleep Deprivation May Lead to Cancer
- Insufficient sleep can be one of the factors that can increase your risk of developing cancer.
- The Journal of Cancer reports that chronic sleep deprivation is associated with incidences of cancer. For example, insomnia or sleep apnea can increase a person’s risk of breast cancer, oral cancer, or prostate cancer.
- Some studies, however, have not found a definite link between the long-term effects of sleep deprivation and cancer. Interestingly, regularly sleeping longer than 8 hours a night could increase the risk of colorectal cancer.
- Regularly getting a good night’s sleep boosts your immune system and helps your body fight disease.
Lack of Sleep May Increase Risk of Death
- Although there is no evidence that you can die directly from a lack of sleep, sleep deprivation can lead to early death.
- A report published in 2010 found that people who averaged 7 hours of sleep every night have the lowest mortality risk. Sleeping less than 7 hours or sleeping longer is associated with an increased risk of dying early. Researchers found that the effects of not getting enough sleep lead to serious health conditions that can shorten your life.
- Poor sleep causes cardiovascular disease, obesity, diabetes, and stress. One or more of these conditions combined can decrease your life expectancy.
Too Little Sleep Causes Chronic Inflammation
- Because a loss of sleep doesn’t allow your body time to repair itself and recharge itself, sleep exhaustion can cause chronic inflammation.
- Inflammation in the short term is necessary to help your body fight disease. However, long-term inflammation can put you at risk of developing chronic diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and heart disease.
- For example, the book StatPearls reports that chronic inflammation is a side effect of chronic sleep disorders. Lack of sleep and stress (that often causes sleepless nights) cause the body to release inflammatory enzymes. One of the ways to combat chronic inflammation is to sleep between 7 and 8 hours every night.
- Research into the long-term effects of sleep deprivation has found that it has the potential to cause mild to moderate organ damage. Sleeping well every night can help to improve your gastrointestinal and cardiovascular health.